Pneumothorax – Causes and Treatment
Primary spontaneous pneumothorax occurs when the formation of sacs of fluid (bronchi) in the chest wall rupture, resulting in air leakage into the chest cavity. The resulting pressure in the chest cavity can cause the chest wall to collapse and result in a full collapse of the lung. A complete collapse can be fatal for those who have not been exposed to adequate amounts of oxygen.
Sometimes fluid from the lungs can remain in the chest wall. This is called secondary spontaneous pneumothorax. When this happens, fluid can fill the airways, making it difficult to breathe, causing apnea or choking. This can often be alleviated by installing an oral airway dilator.
Primary spontaneous pneumaxia is more common than most people think. Although it has no symptoms, it is often difficult to diagnose. With age, the patient may experience more severe symptoms, which may indicate the presence of pneumonia or lung cancer. If left untreated, it can also be dangerous due to its potentially lethal nature.
Two types of treatment are available: oxygen therapy and mechanical ventilation. A patient who is experiencing sudden onset of coughing with wheezing or without and experiencing chest pain, usually in the right upper quadrant of the chest, should consult with their doctor immediately. In many cases, patients with secondary spontaneous pneumaxis can be treated with antibiotics.
If the patient has these symptoms, surgery may be required. If the patient has already had a complete collapse of the lung or has another serious problem, the doctor may recommend a lung transplant to save the patient's life.
There are two types of pneumothorax surgery: open and laparoscopic. The laparoscopic technique involves the placement of an instrument called a cannula in the mouth and nose to provide the patient with controlled ventilation. The laparoscope is also used to guide the surgeon through the surgical procedure.
The laparoscopic approach involves the use of instruments that are less complicated than the conventional approach in order to provide a simpler and faster procedure.
Because the patient is not in the same position during the procedure, there is less risk of injury to vital organs
Another difference between the laparoscopic and traditional techniques is that the laparoscopic technique is less intrusive and involves less time in recovery. Some patients are able to return to their normal activities within a few hours following the procedure.
Primary spontaneous pneumax requires immediate attention in order to prevent any complications from occurring. Patients who do not receive prompt medical attention can suffer from complications such as breathing difficulties, pneumonia, and even pneumonia. This complication can cause death or permanent damage to the lungs.
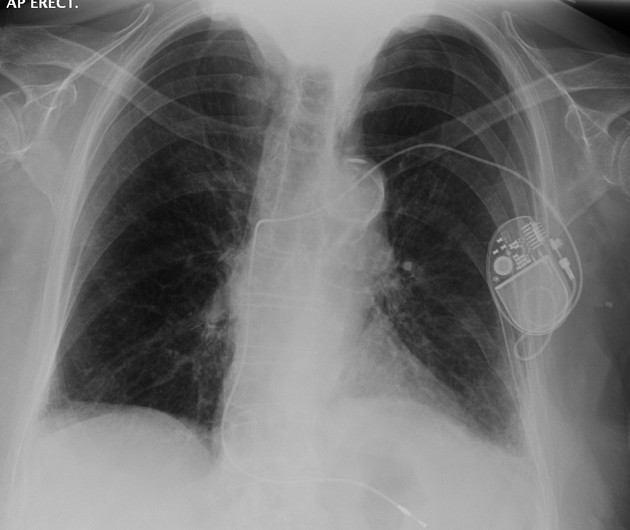
During the procedure, chest x-rays and CT scans will be taken in order to determine the cause of the pneumothorax and to rule out complications. If there is no obstruction in the airway, a bronchoscope can be used to provide additional oxygen to the lung.
Because a patient will experience pain during the procedure, the physician may recommend a more invasive procedure to remove as much of the lung as possible. In some cases, the lung may need to be removed through the abdominal cavity.
After the procedure, the patient may not feel any discomfort. However, because the lung is exposed and the chest x-rays will not show any visible evidence of the procedure, the patient may feel tired and fatigued.
It is important to monitor the pulmonary function in the days following the procedure to monitor for any complication. Although most patients will return to normal within a few days, it is always better to err on the side of caution and take action if there is a danger of the lung collapsing or the airway becoming blocked.